우선 Scope에 대해 알아보자.
function outer() {
let a = 1;
console.log(a);
}
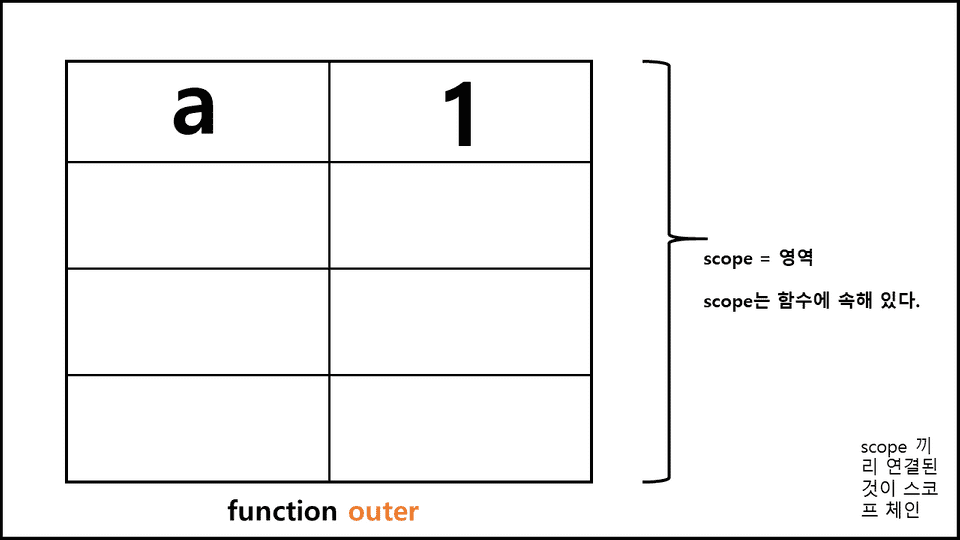
outer();a에는 무슨 값이 들어있을까 하고 무슨 값이 들어 있는지 찾는 곳이 바로 Scope다. 일종의 표가 있다고 하자.
위 표가 function outer 의 scope가 된다. 여러 함수가 들어 있다면 scope에 추가 될 것이다.
※ scope는 함수 단위로 적용된다.
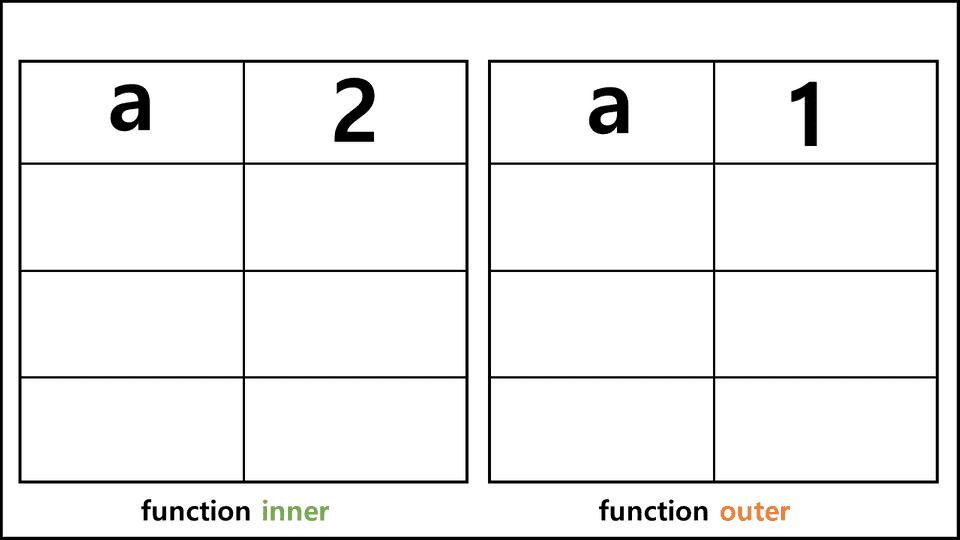
예를 들어 outer함수 내부에 inner라는 함수를 넣었을 때는 scope는 어떻게 될까 ?
function outer() {
let a = 1;
function inner() {
let a = 2;
console.log(a);
}
inner();
}
outer();위 그림 처럼 될 것이다.
inner가 a를 찾을 때, 들여다보는 표가 바로 scope이다.
조금 더 나아가보자.
function outer() {
let a = 1;
let b = "영준";
function inner() {
let a = 2;
console.log(b);
}
inner();
}
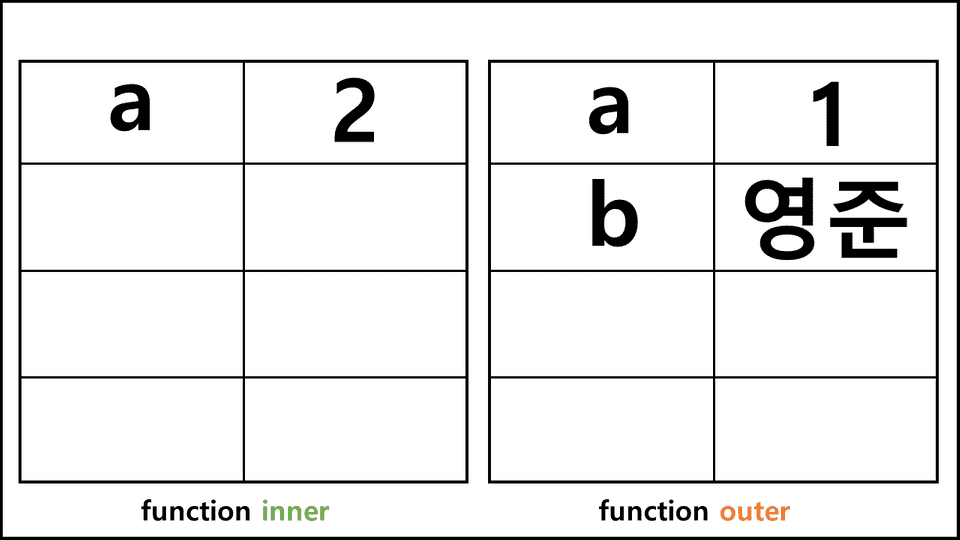
outer();outer안에 b가 선언되었고, inner안에서 console.log(b)를 입력했다.
그러면 inner는 b를 어떻게 찾을까?
먼저 그림과 같이
outer의 scope에 b가 들어가 있을 것이고, inner에서는 b가 없다.
어떻게 b를 찾는지 순서를 보면,
inner의scope에서b가 있는지 찾아본다.b가 없으니inner가 태어난 곳 바로 윗단계인outer에서 찾는다.outer의scope에는b가 있으니,console.log(b)를 실행.
위 순서대로 scope를 조사하여 찾는다. 그럼 만약에
let c = "병민";
function outer() {
let a = 1;
let b = "영준";
function inner() {
let a = 2;
console.log(c);
}
inner();
}
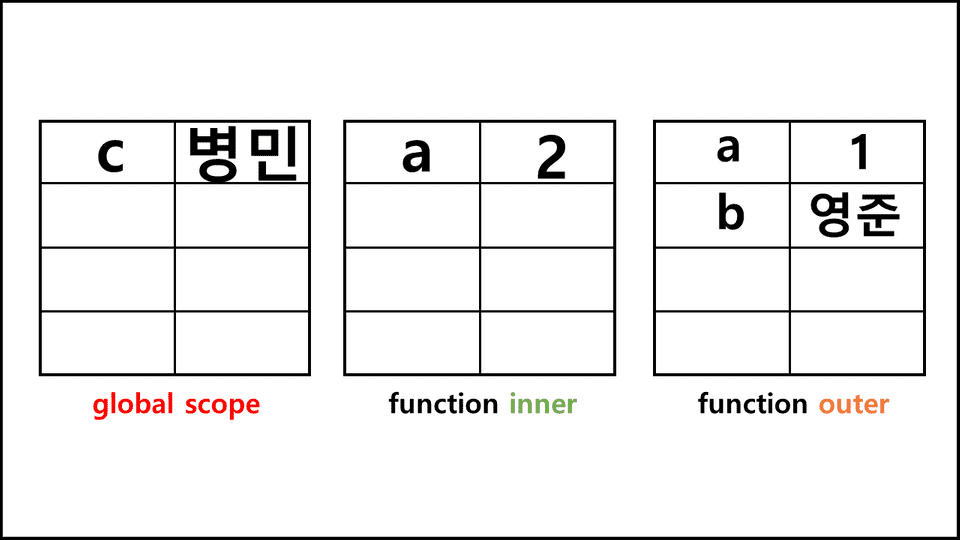
outer();위와 같은 상태면 어떻게 될까 ?? 여기서 c는 outer 함수안에 있지도 않다.
그림으로 그려보면,
inner scope -> outer scope -> global scope 순서대로 찾게 된다.
이렇게 연결된 것이 바로 scope chain이다.
이제 closure를 살펴보자.
1 let c = "병민";
2
3 function outer() {
4 let a = 1;
5 let b = "영준";
6
7 function inner() {
8 let a = 2;
9 console.log(b);
10 }
11 return inner;
12 }
13 let test = outer();
14 test();코드해석 : outer() 가 하는 일은 line3 ~ line10을 지나 line 11 에서 inner를 return 하고, 그 다음 inner 에서는 line9 에서 console.log(b)를 실행하는데, 이때 b는 outer에 있는 영준이다.
line13의test는outer()에서inner를 받게된다.- 그다음, 받게 된
inner를test()에서 실행하게 된다.
클로저 설명
outer의 b가 사라지는게 아니고, inner가 b를 사용할 때에도 scope chain을 가지고 다닌다. 라는게 closure 이다.
즉, line13에서 outer()를 test라는 이름에 담은 뒤에도, scope chain 이 살아있다.
밖으로 꺼낸 뒤에도, outer 가 실행되고 끝난 뒤에도 scope에 접근할 수 있는 것.